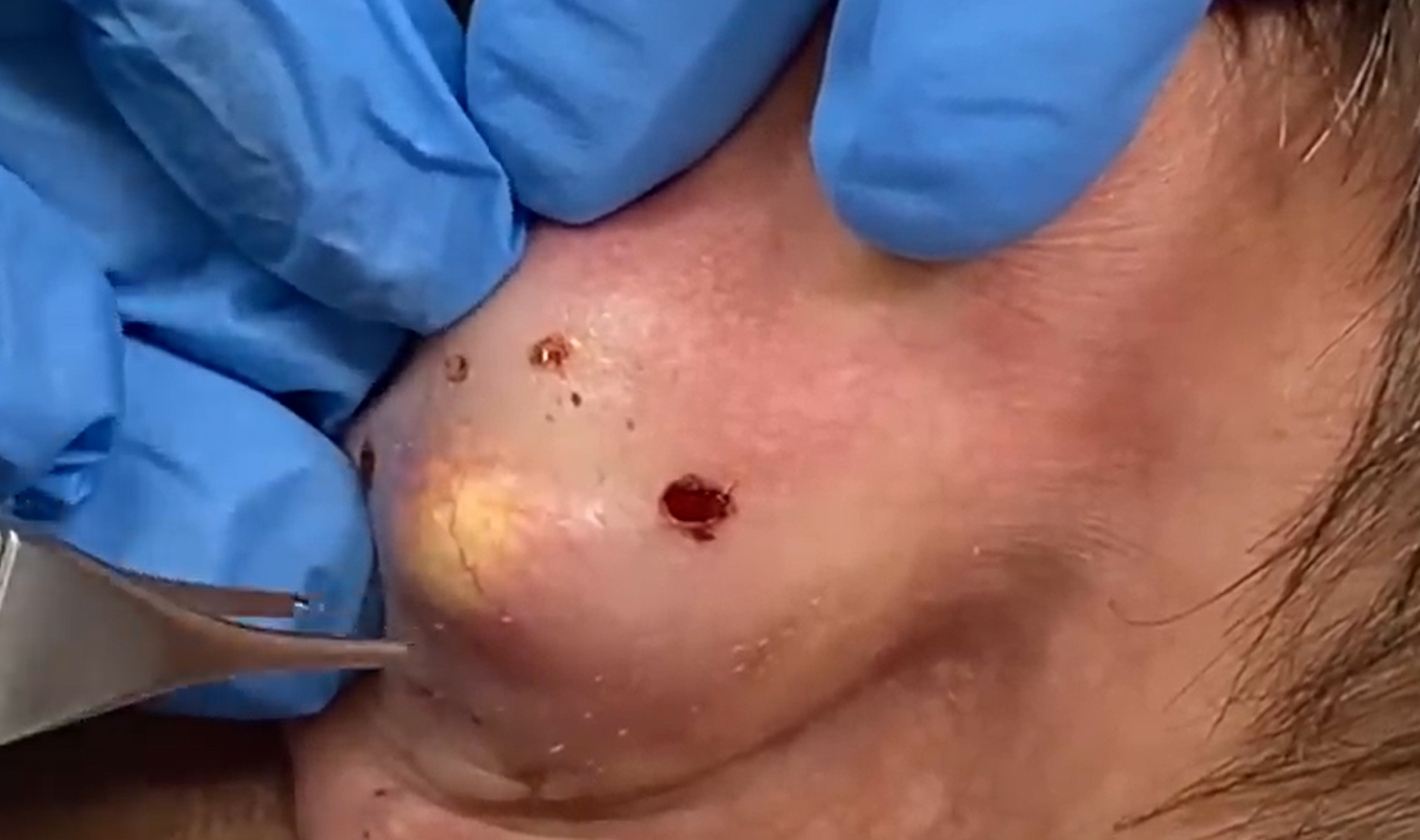
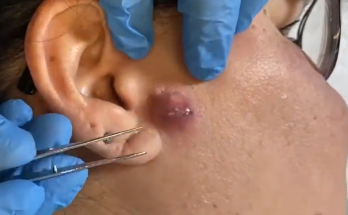
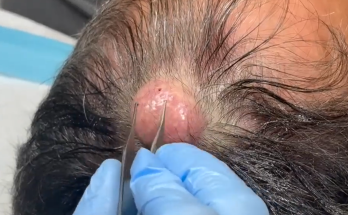
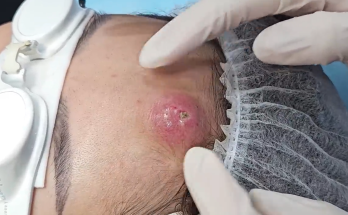
Removal of the ear’s epidermal cyst with a commitment to prevent recurrence and scarring
The removal of an epidermal cyst from the ear requires precision to ensure complete excision while minimizing the risk of recurrence and scarring. Here’s the best approach:
1. Preoperative Considerations
- Assessment: Confirm the diagnosis through clinical examination. If needed, use ultrasound to assess the cyst depth.
- Patient Preparation: Advise the patient on the procedure, risks, and post-operative care.
- Sterilization: Clean the area with an antiseptic solution (chlorhexidine or povidone-iodine).
2. Surgical Removal
- Anesthesia: Local anesthesia (lidocaine with epinephrine) to minimize bleeding and pain.
- Incision Choice:
- If the cyst is small and intact, a minimal excision technique using a small incision over the cyst may allow for easy removal.
- For larger cysts, an elliptical incision around the cyst with an undermining approach is recommended.
- Complete Excision: The entire cyst, including its capsule, must be removed to prevent recurrence. Avoid rupture of the cyst to minimize inflammation.
- Hemostasis: Cauterization or pressure control bleeding.
3. Closure and Scar Prevention
- Minimal Suturing: Use fine sutures (e.g., 6-0 or 7-0 non-absorbable) to reduce scarring.
- Wound Edges Approximation: Avoid excessive tension to prevent hypertrophic scarring.
- Topical Scar Prevention: Consider silicone gel or sheets post-healing.
4. Postoperative Care
- Antibiotics (if needed): If infection risk is high, a short course of antibiotics may be prescribed.
- Wound Care: Keep the area clean and dry; apply antibiotic ointment.
- Follow-up: Monitor for signs of infection or recurrence.
Would you like additional details on a specific part of the procedure?