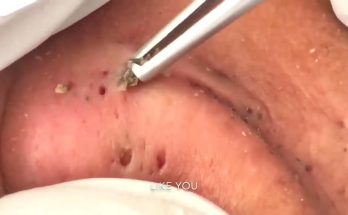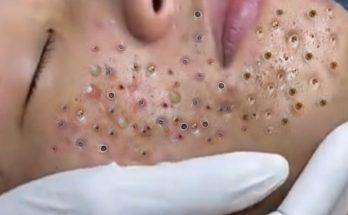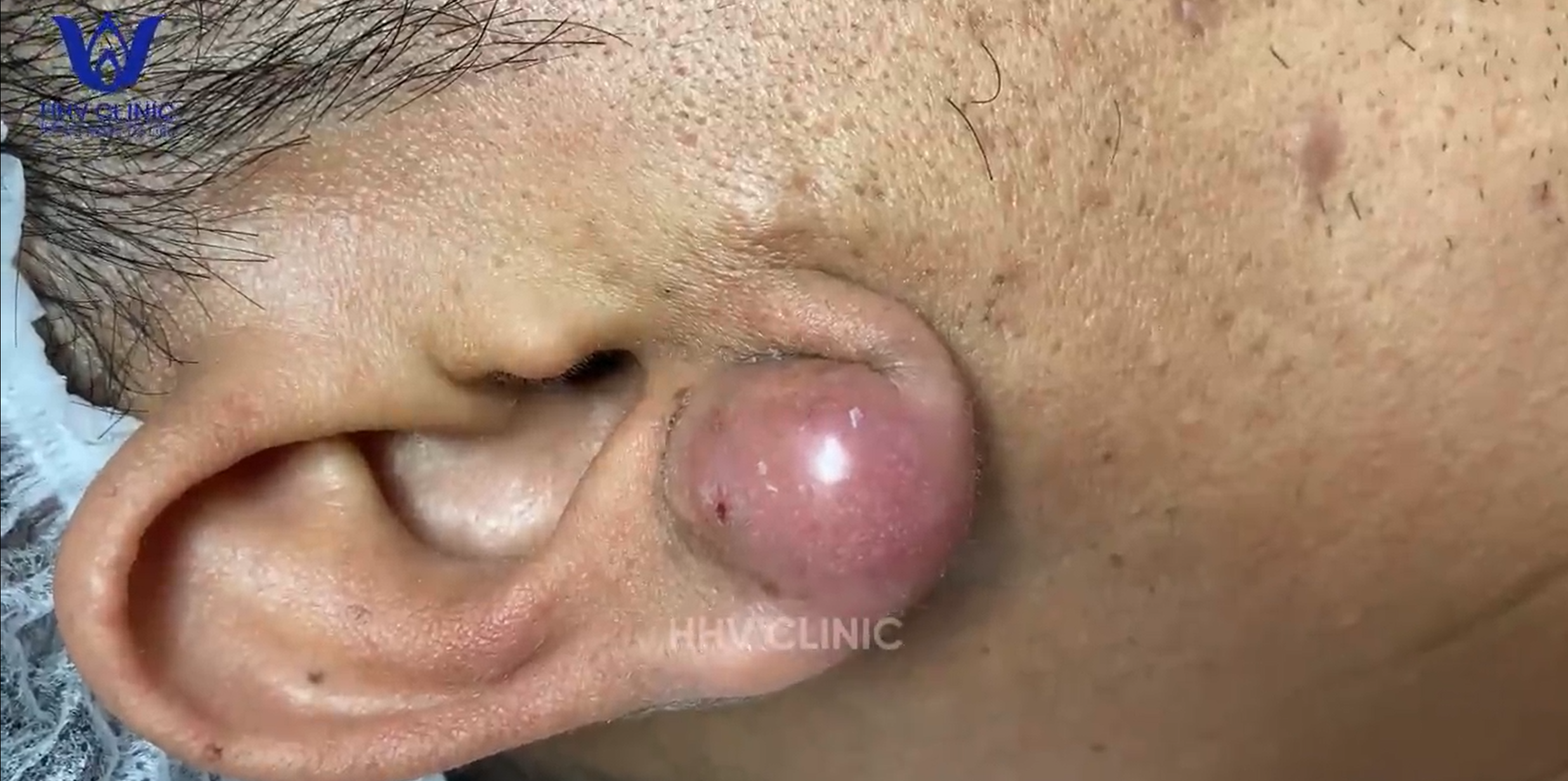
TREATMENT OF PIMPLES (ABSCESSES IN THE EAR AREA) IS COMMITTED TO NOT RECURRING, NOT LEAVING SCARS
Treating pimples or abscesses in the ear area requires special care to prevent recurrence, minimize scarring, and promote proper healing. Abscesses in the ear can be painful and uncomfortable, and addressing them the right way is essential for optimal recovery. Here’s what you should know:
1. Consult a Professional (Clinic Visit)
- It’s crucial to seek medical attention from a healthcare provider or dermatologist for proper diagnosis and treatment, especially if the abscess is painful, large, or recurring.
- Why? Self-treatment can lead to complications like infection spread, improper drainage, or scarring.
2. Understanding Abscesses in the Ear Area
- Abscesses are typically caused by bacterial infections, often from blocked pores or hair follicles, leading to the formation of pus.
- They can occur in the ear canal or outer ear area, with swelling, redness, and pain as common symptoms.
3. Treatment Options for Abscesses
- Drainage: In a clinical setting, a doctor may perform an incision and drainage procedure if the abscess is large and painful. This helps remove pus and relieve pressure, promoting faster healing.
- Antibiotics: Oral or topical antibiotics may be prescribed to control the infection and prevent it from spreading. Follow the prescribed course to ensure the infection is fully eradicated.
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relief (like ibuprofen) can help alleviate discomfort, but only use as directed by a healthcare professional.
4. Avoiding Recurrence
- Proper Hygiene: Keeping the ear clean and dry is essential. Use gentle cleansers and avoid inserting objects into the ear that could irritate or introduce bacteria.
- Avoid Squeezing: Do not attempt to pop or squeeze an abscess, as this can push bacteria deeper into the skin, leading to further infection or scarring.
- Moisturization: If your skin is prone to acne or abscesses, using a non-comedogenic moisturizer may help prevent blockages in the ear area.
5. Prevention of Scarring
- Timely Treatment: Early intervention can prevent the abscess from becoming too large and reducing the risk of scarring.
- Follow-Up Care: After the abscess is drained or treated, your doctor may recommend gentle wound care or topical treatments to promote healing and reduce the risk of scarring.
6. Post-Treatment Care
- Follow all aftercare instructions given by your healthcare provider.
- Avoid exposing the treated area to excessive moisture or irritation.
- In some cases, scar treatments like silicone gel sheets or creams might be recommended to minimize scarring after healing.
7. When to Seek Further Medical Help
- If the abscess recurs despite treatment, it may be necessary to explore underlying causes, such as chronic skin conditions (e.g., acne, eczema) or recurrent infections.
- If there are signs of complications like fever, increased redness, or spreading infection, seek medical attention immediately.
By following the proper treatment regimen at a clinic and taking steps to prevent recurrence and scarring, you can manage abscesses in the ear area effectively. Always consult with a healthcare professional for guidance on treatment and recovery.